Influence of Scratch on the Crack Pattern of Monolithic Glass under Flexural Loading
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.47982/cgc.9.504Downloads
Abstract
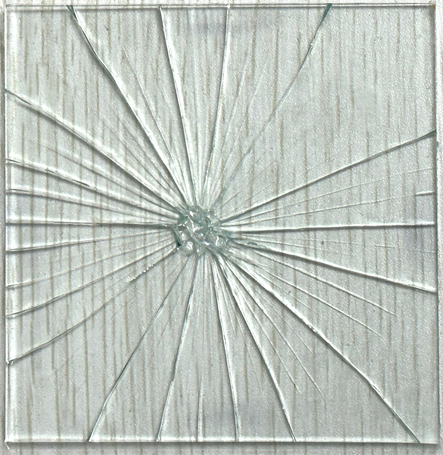
Scratch-induced surface damage of aged glass elements can lead to strength degradation of glass material and thus threatens the safety of architectural glass. It is of significance to evaluate the mechanical performance of scratched glass elements. In this study, deep close-to-reality scratch is introduced at the centre of the annealed glass plate by a diamond indenter. Coaxial double ring (CDR) test is conducted to evaluate the flexural performance of scratched glass. The test setup is based on EN 1288-5 standard and the specimens are square size for convenience. A total number of 40 glass plates are tested consisting of intact and scratched specimens with two typical loading rates. Test results show that the loading rate will lead to the variation of material strength but will not significantly influence the crack pattern for both intact and scratched glass. To have a thorough understanding of the fracture process of scratched monolithic glass, numerical simulation of CDR test is performed based on the peridynamics (PD) theory. The scratch features in the model are simplified to improve the computational efficiency. Deflection Results obtained from the plate theory are used to validate the PD model. The initiation and propagation of radial cracks along the surface are captured. Such research findings can contribute to the fracture behaviour evaluation of scratched glass elements.
Published
Issue
Section
Strength, Stability & Safety
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Zhufeng Pan, Jian Yang, Xing-er Wang, Gang Li, Xianfang Jiang

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.



