Examination of the Load-Bearing Behavior of a Bonded Edge Seal for Fluid-Filled Insulating Glass Units
Downloads
Abstract
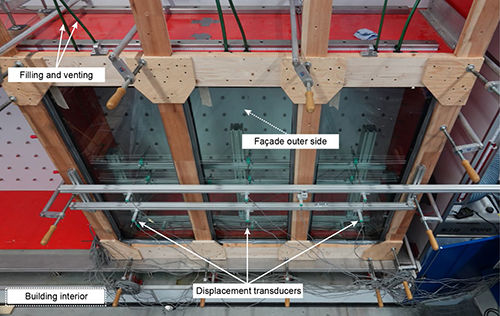
This paper presents a study on the development of a bonded edge seal for fluid-filled insulating glass units. Such novel façade elements enable multifunctional building envelopes and an improved energy efficiency of buildings. The bonded edge seal of a fluid-filled glazing is highly stressed due to the hydrostatic pressure that acts in addition to typical loads on façades. The permanent exposure to the fluid may also cause severe aging effects. Therefore, the edge seal is designed in such a way that the chemical and physical stress splits on two functional zones. The first functional zone serves as a protective seal and separates the fluid from the second, load-bearing functional zone. The adhesives for both functional zones were selected using an extensive test program. Once the materials have been selected, the novel façade elements are tested in large scale component tests. The mock-ups are built on a scale of 1:2 compared to the original size of the intended façade elements. Since the study focuses on the performance of the adhesively bonded edge, the edge detail is realized in original size while the glass size is smaller. The glass thickness is modified to achieve rotations in the edge zone that correspond to façade elements in original size. The tests are performed in a test rig for curtain walls, which allows the simultaneous loading of the element by cyclic wind pressure and constant water pressure. The adhesive bond carries all the loads except the deadweight of the glass panes. The test results are compared with the numerical calculations and an estimate of the load-bearing behaviour is made.
Published
Issue
Section
CertBond COST Action CA18120
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Alina Joachim, Felix Nicklisch, Alexander Freund, Bernhard Weller

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.



