The Numerical analysis and experimental verification on the thermal performance of hybrid Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT)-glass facade elements
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.7480/cgc.7.4459Downloads
Abstract
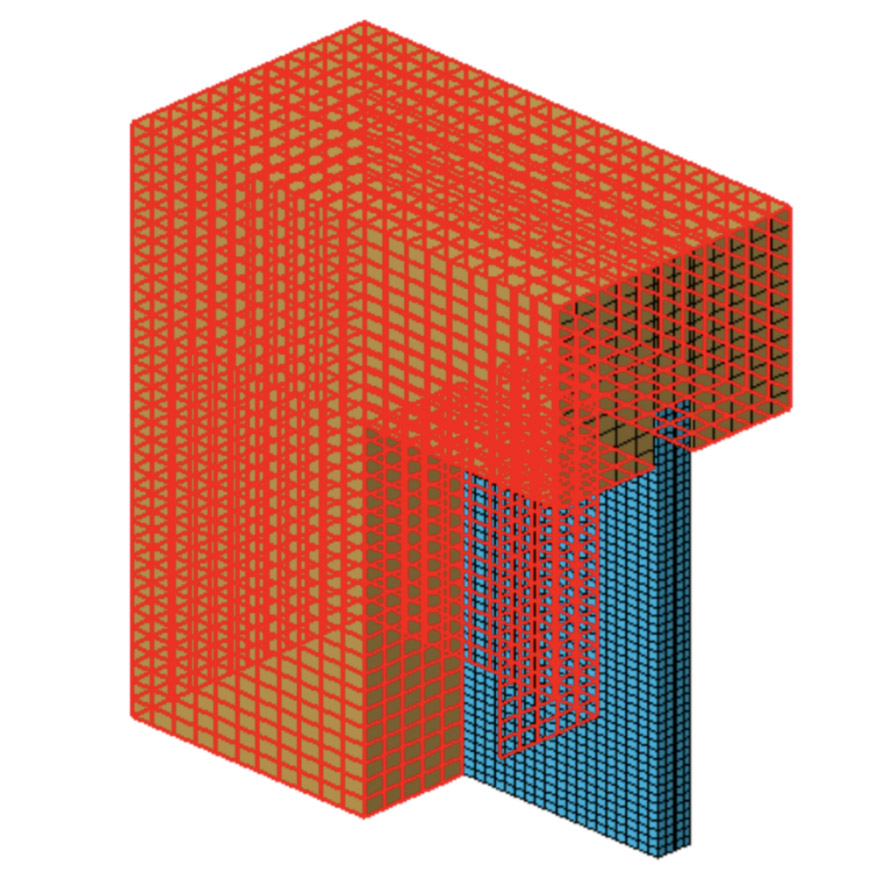
Structural solutions involving the mechanical interaction of timber and glass load-bearing members showed a progressive increase in the last decade. Among others, a multipurpose hybrid facade element composed of Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT) members and glass panels interacting by frictional contact mechanisms only was proposed ion the framework of the VETROLIGNUM project. While demonstrating enhanced load-bearing and deformation capacity performances under seismic loads, facade elements are known to represent a building component with multiple performance parameters to satisfy. These include energy efficiency, durability, lightening comfort and optimal thermal performance. In this paper, a special focus is dedicated to the thermal performance assessment of CLT-glass facade modules under ordinary operational conditions. Based on the thermal-chamber analysis of small-scale prototypes, reliable Finite Element numerical models are developed and applied to full-scale VETROLIGNUM solution. Sensitivity analyses are hence carried out to explore the actual thermal performance of these novel hybrid systems.
Published
Issue
Section
Hybrid & Composite Glass Components
Keywords:
Cross laminated timber CLT, structural glass, CLT - structural glass hybrid facade, thermal performance, small-scale experiments, Finite Element numerical modellingLicense
Copyright (c) 2020 Vlatka Rajčić, Chiara Bedon, Jure Barbalic, Nikola Perkovic

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.



