Abstract
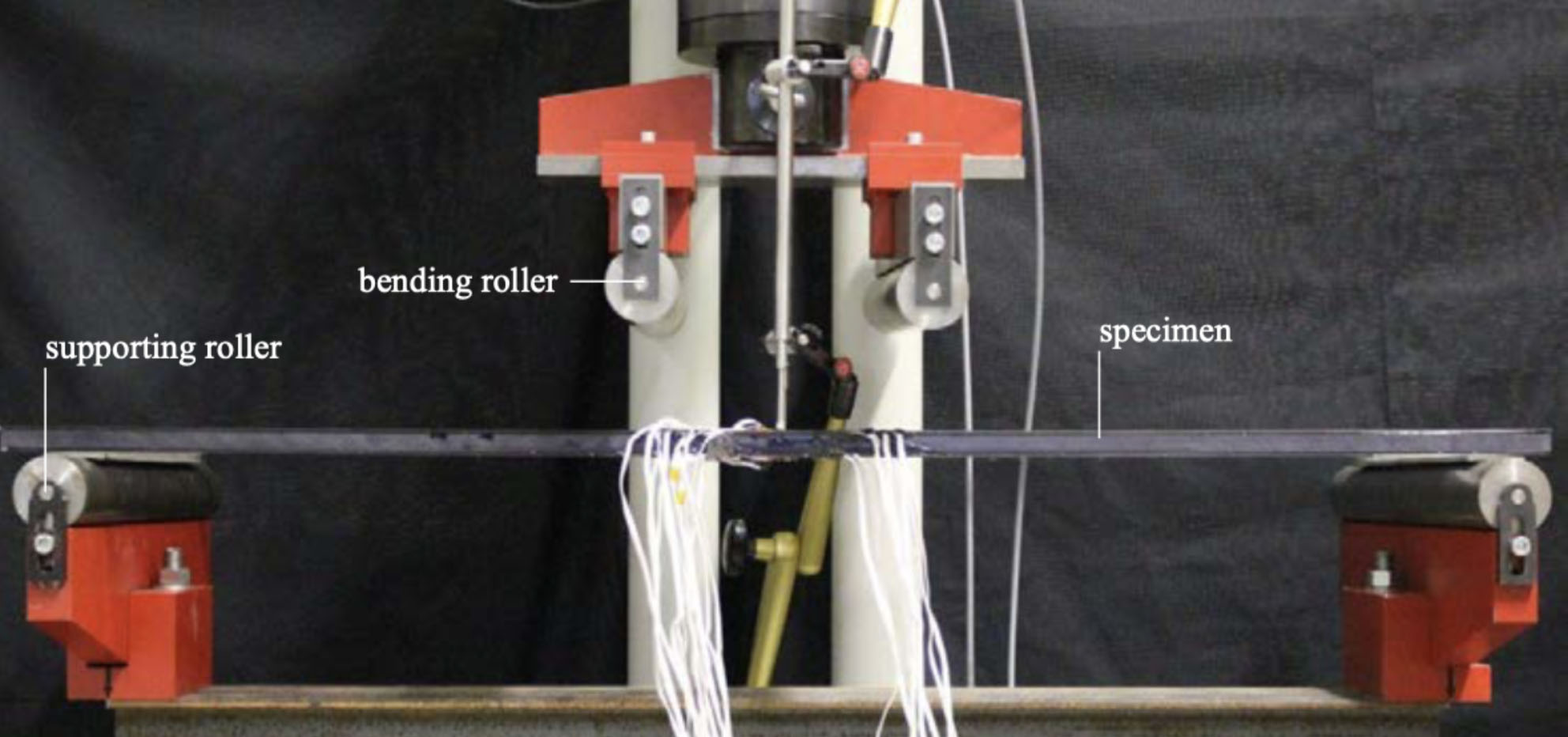
Innovative glazing, which combines polycarbonate and thin glass to composite panels, ensures a slighter alternative to glass laminates with a high resistance against manual attack. Due to experimental studies, these thin glass-polycarbonate composite panels are classified as laminated safety glass and security glazing. The study describes analytical models to analyse their structural behaviour for static short time loads. In accordance to the geometrical boundary conditions of the four-point bending test, the composite panel can be described by the beam theory. A multi-layered system is calculated with the sandwich beam theory with a bending and shear deformation. Additionally, an extended approximate solution based on Wölfel is compared to the classical theory of sandwich elements as well as with experimental results.
Published
Issue
Section
Laminated Glass & Interlayer Properties
Keywords:
Thin Glass, Polycarbonate, Composite Panel, Sandwich TheoryLicense
Copyright (c) 2020 Sebastián Andrés López, Thorsten Weimar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.