Combined Voronoi-FDEM approach for modelling post-fracture response of laminated tempered glass
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.7480/cgc.7.4737Downloads
Abstract
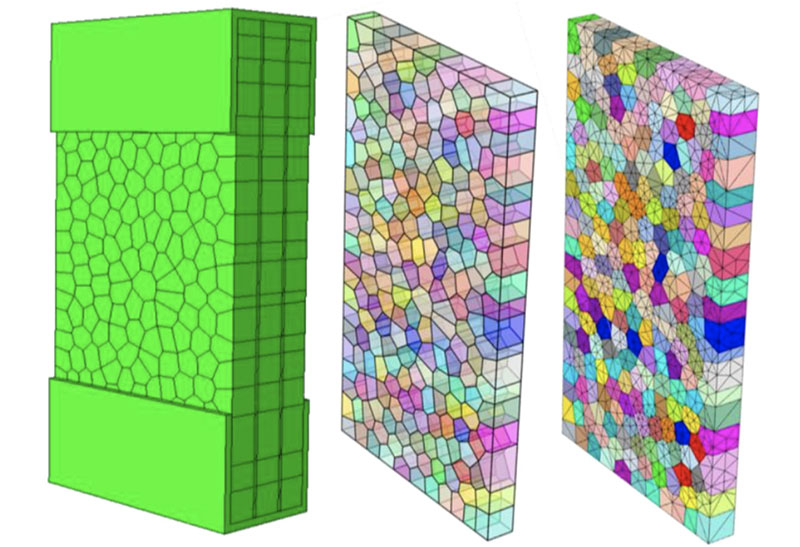
In this work, a combined Voronoi and finite-discrete element method (FDEM) approach for reconstructing the post-fracture model of laminated glass (LG) was proposed. The fracture morphology was determined via introducing Voronoi tessellation with statistical distribution parameters such as the fragment face numbers, volume and sphericity. The residual interaction between glass fragments was described with cohesive zone model. One fractured LG block under uniaxial tension, which was taken from a triple layered LG beam with ionoplast interlayers, was modelled and validated with experimentally recorded data. Through iteration analysis, the key cohesive parameters were determined for the most applicable model. It is followed by investigating the influence due to the fragments interaction property. The results show that the cohesion and frictional property can be combined to well describe the residual interaction behaviour between fragments. The frictional property has a remarkable effect on the post-fracture resistance whereas the associated effect on the stiffness is not evident. Compared to other cohesive parameters, the cohesive stiffness factors present predominant effect on both the post-fracture stiffness and resistance.
Published
Issue
Section
Numerical Modeling & Experimental Validation
Keywords:
Laminated glass, Tempered glass, Post-fracture response, Voronoi tessellation, Fracture morphologyLicense
Copyright (c) 2020 Xing-er Wang, Jian Yang, Zhufeng Pan, Yuhan Zhu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.



